3D models of early strepsirrhine primate teeth from North Africa
3D models of Pontognathus ignotus and Massetognathus pascuali
3D models of Protosilvestria sculpta and Coloboderes roqueprunetherion
3D GM dataset of bird skeletal variation
Skeletal embryonic development in the catshark
Bony connexions of the petrosal bone of extant hippos
bony labyrinth (11) , inner ear (10) , Eocene (8) , South America (8) , Paleobiogeography (7) , skull (7) , phylogeny (6)
Lionel Hautier (22) , Maëva Judith Orliac (21) , Laurent Marivaux (16) , Rodolphe Tabuce (14) , Bastien Mennecart (13) , Pierre-Olivier Antoine (12) , Renaud Lebrun (11)
MorphoMuseuM Volume 08, issue 03
<< prev. article next article >>
|
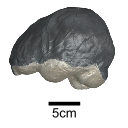
Original articleThe endocranial cast of a 10 ka intentionally deformed human cranium from ChinaYin Qiyu
Published online: 27/07/2022 |

|
M3#972The frontal region of the endocast is flattened, probably formed by the constant pressure on the frontal bone during growth. There is a well-developed frontal crest on the endocranial surface. The endocast widens posteriorly from the frontal lobe. The widest point of the endocast is at the lateral border of the parietal lobe. The lower parietal areas display a marked lateral expansion. The overall shape of the endocast is asymmetrical, with the left side of the parietal lobe being more laterally expanded than the right side. Like the frontal lobe, the occipital lobe is also anteroposteriorly flattened. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.972 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#976The original endocranial cast model (with texture) of IVPP-PA1616. It shows the original structures of the specimen, and was not altered in any way. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.976 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Beaudet, A., Clarke, R. J., de Jager, E. J., Bruxelles, L., Carlson, K. J., Crompton, R., de Beer, F., Dhaene, J., Heaton, J. L., Jakata, K., Jashashvili, T., Kuman, K., McClymont, J., Pickering, T. R., Stratford, D., 2019. The endocast of StW 573 (“Little Foot”) and hominin brain evolution. Journal of Human Evolution 126, 112-123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2018.11.009.
Dean, V., 1995. Sinus and meningeal vessel pattern changes induced by artificial cranial deformation: A pilot study. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology 5, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1002/oa.1390050102.
Dean, V., 1996. Comparative endocranial vascular changes due to craniosynostosis and artificial cranial deformation. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 101(3), 369-385. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-8644(199611)101:3<369::AID-AJPA6>3.0.CO;2-U.
Neubauer, S., Gunz, P., Leakey, L., Leakey, M., Hublin, J.-J., Spoor, F., 2018. Reconstruction, endocranial form and taxonomic affinity of the early Homo calvaria KNM-ER 42700. Journal of Human Evolution 121, 25-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2018.04.005.
Tubbs, R. S., Salter, G., Oakes, W., 2006. Artificial deformation of the human skull: A review. Clinical anatomy (New York, N.Y.) 19, 372-377. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20177.
Yin, Q., Li, Q., Zhang, H., Ma, N., Zhang, W., Ni, X., 2020. A 10 ka intentionally deformed human skull from Northeast Asia. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology https://doi.org/10.1002/oa.3104.
Zollikofer, C. P. E., De León, M. S. P., 2013. Pandora's growing box: Inferring the evolution and development of hominin brains from endocasts. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews 22(1), 20-33. https://doi.org/10.1002/evan.21333.