Explodable 3D Dog Skull for Veterinary Education
3D models of a Sheep and Goat Skull and Inner ear
3D models of Miocene vertebrates from Tavers
3D GM dataset of bird skeletal variation
Skeletal embryonic development in the catshark
Bony connexions of the petrosal bone of extant hippos
bony labyrinth (11) , inner ear (10) , Eocene (8) , South America (8) , Paleobiogeography (7) , skull (7) , phylogeny (6)
Lionel Hautier (23) , Maëva Judith Orliac (21) , Laurent Marivaux (16) , Rodolphe Tabuce (14) , Bastien Mennecart (13) , Renaud Lebrun (12) , Pierre-Olivier Antoine (12)
MorphoMuseuM Volume 01, Issue 04:April 2016
|
Skeletogenesis during the late embryonic development of the catshark Scyliorhinus canicula (Chondrichthyes; Neoselachii)Sébastien Enault, Sylvain Adnet
Published online: 25/04/2016 |

|
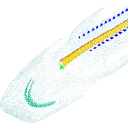
M3#50Mineralized skeleton of a 6,2 cm long embryo of Scyliorhinus canicula Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.50 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Scyliorhinus canicula SC6_7_2015_03_20 View specimen
|
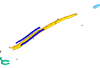
M3#51Mineralized skeleton of a 6,7 cm long embryo of Scyliorhinus canicula Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.51 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Scyliorhinus canicula SC7_1_2015_04_03 View specimen
|
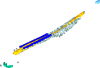
M3#52Mineralized skeleton of a 7,1 cm long embryo of Scyliorhinus canicula Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.52 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Scyliorhinus canicula SC7_5_2015_03_13 View specimen
|
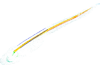
M3#53Mineralized skeleton of a 7,5 cm long embryo of Scyliorhinus canicula Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.53 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Scyliorhinus canicula SC8_2015_03_20 View specimen
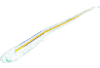
|
M3#54Mineralized skeleton of a 8 cm long embryo of Scyliorhinus canicula Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.54 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Scyliorhinus canicula SC10_2015_02_27 View specimen
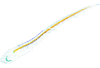
|
M3#55Mineralized skeleton of a 10 cm long embryo of Scyliorhinus canicula Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.55 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
3D models related to the publication: Morphogenesis of the liver during the human embryonic periodAyumi Hirose
Published online: 17/03/2016 |

|
M3#64Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 14 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.64 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS15LIV5074 View specimen

|
M3#65Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 15 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.65 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS16LIV2578 View specimen

|
M3#66Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 16 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.66 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS17LIV17832 View specimen

|
M3#67Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 17 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.67 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS18LIV21124 View specimen

|
M3#68Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 18 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.68 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS19LIV14353 View specimen

|
M3#69Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 19 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.69 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS20LIV20701 View specimen

|
M3#70Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 20 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.70 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS21LIV25858 View specimen

|
M3#71Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 21 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.71 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS22LIV22226 View specimen

|
M3#72Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 22 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.72 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS23LIV25704 View specimen

|
M3#73Human liver at Carnegie Stage (CS) 23 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.73 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
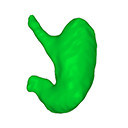
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in: Kaigai N et al. Morphogenesis and three-dimensional movement of the stomach during the human embryonic period, Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014 May;297(5):791-797. doi: 10.1002/ar.22833.
Homo sapiens KC-CS16STM27159 View specimen
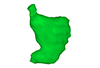
|
M3#56computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#56_KC-CS16STM27159) at Carnegie Stage 16 (Crown Rump Length= 9.9mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf56 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS17STM20383 View specimen

|
M3#57computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#57_KC-CS17STM20383) at Carnegie Stage 17 (Crown Rump Length= 12.3mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf57 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS18STM21807 View specimen

|
M3#58computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#58_KC-CS18STM21807) at Carnegie Stage 18 (Crown Rump Length= 14.7mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf58 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS19STM17998 View specimen

|
M3#59computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#59_KC-CS19STM17998) at Carnegie Stage 19 (Crown Rump Length was unmeasured ). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf59 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS20STM20785 View specimen

|
M3#60computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#60_KC-CS20STM20785) at Carnegie Stage 20 (Crown Rump Length= 18.7 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf60 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS21STM24728 View specimen

|
M3#61computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#61_KC-CS21STM24728) at Carnegie Stage 21 (Crown Rump Length= 20.9 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf61 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS22STM26438 View specimen

|
M3#62computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#62_KC-CS22STM26438) at Carnegie Stage 22 (Crown Rump Length= 21.5 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf62 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS23STM20018 View specimen

|
M3#63computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#63_KC-CS23STM20018) at Carnegie Stage 23 (Crown Rump Length= 23.1 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf63 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |