Explodable 3D Dog Skull for Veterinary Education
3D models of a Sheep and Goat Skull and Inner ear
3D models of Miocene vertebrates from Tavers
3D GM dataset of bird skeletal variation
Skeletal embryonic development in the catshark
Bony connexions of the petrosal bone of extant hippos
bony labyrinth (11) , inner ear (10) , Eocene (8) , South America (8) , Paleobiogeography (7) , skull (7) , phylogeny (6)
Lionel Hautier (23) , Maëva Judith Orliac (21) , Laurent Marivaux (16) , Rodolphe Tabuce (14) , Bastien Mennecart (13) , Renaud Lebrun (12) , Pierre-Olivier Antoine (12)

|
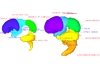
3D models related to the publication: Morphology of the human embryonic brain and ventriclesNaoki Shiraishi
Published online: 27/07/2015 |
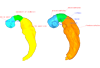
|
M3#24Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 13. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf24 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS14BRN18834 View specimen
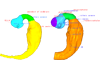
|
M3#25Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 14. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf25 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS15BRN19975 View specimen
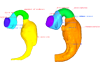
|
M3#26Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 15. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf26 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS16BRN7870 View specimen
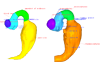
|
M3#27Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 16. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf27 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS17BRN26702 View specimen

|
M3#28Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 17. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf28 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS18BRN25914 View specimen

|
M3#29Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 18. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf29 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS19BRN16508 View specimen

|
M3#30Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 19. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf30 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS20BRN26581 View specimen

|
M3#31Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 20. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf31 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS21BRN33434 View specimen
|
M3#32Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 21. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf32 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS22BRN27960 View specimen

|
M3#33Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 22. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf33 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS23BRN28189 View specimen
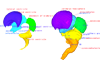
|
M3#34Computationally reconstructed cerebral parenchyma and ventricle of the human embryo at Carnegie Stage 23. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf34 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains sixteen 3D models of unornamented Polygnathus illustrating allometric variation and bilateral asymmetry within four “Operational Taxonomic Units” analyzed in the publication: Convergent allometric trajectories in Devonian-Carboniferous unornamented Polygnathus conodonts.
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-010 View specimen

|
M3#1611Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1611 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-011 View specimen

|
M3#1612Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1612 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-012 View specimen

|
M3#1613Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1613 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-013 View specimen

|
M3#1614Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1614 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-014 View specimen

|
M3#1615Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1615 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-015 View specimen

|
M3#1616Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1616 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-016 View specimen

|
M3#1617Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1617 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-017 View specimen

|
M3#1618Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1618 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-018 View specimen

|
M3#1619Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1619 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-019 View specimen

|
M3#1620Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1620 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-020 View specimen

|
M3#1621Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1621 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-021 View specimen

|
M3#1622Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1622 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-022 View specimen

|
M3#1623Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1623 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-023 View specimen

|
M3#1624Sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1624 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-024 View specimen

|
M3#1625Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1625 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Polygnathus sp. UM-PSQ-025 View specimen

|
M3#1626Dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1626 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models of the holotype and the paratypes of the new species Siphonodella leiosa described and analyzed in the following publication: L. Souquet, C. Corradini, C. Girard: Siphonodella leiosa (Conodonta), a new unornamented species from the Tournaisian (lower Carboniferous) of Puech de la Suque (Montagne Noire, France). Geobios, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geobios.2020.06.004.
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 1 View specimen

|
M3#525Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.525 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 2 View specimen

|
M3#526Siphonodella leiosa, holotype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.526 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 3 View specimen

|
M3#527Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.527 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 4 View specimen

|
M3#528Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.528 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 5 View specimen

|
M3#529Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.529 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 6 View specimen

|
M3#530Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.530 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 7 View specimen

|
M3#531Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.531 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 8 View specimen

|
M3#532Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.532 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 9 View specimen

|
M3#533Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.533 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models of Protocetus atavus described and figured in the following publication: Berger et al. (2025) The endocranial anatomy of Protocetids and its implications for early whale evolution.
Protocetus atavus SMNS-P-11084 View specimen

|
M3#1654Textured model of the whole skull Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1654 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#1655Brain endocast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1655 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
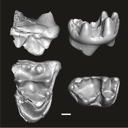
This contribution contains the three-dimensional digital models of eleven isolated fossil teeth of a merialine paroxyclaenid (Welcommoides gurki), discovered from lower Oligocene deposits of the Bugti Hills (Balochistan, Pakistan). These fossils were described, figured and discussed in the following publication: Solé et al. (2024), An unexpected late paroxyclaenid (Mammalia, Cimolesta) out of Europe: dental evidence from the Oligocene of the Bugti Hills, Pakistan. Papers in Palaeontology. https://doi.org/10.1002/spp2.1599
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2225 View specimen
|
M3#1083Left m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1083 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2226 View specimen
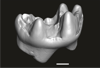
|
M3#1084Right m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1084 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2227 View specimen
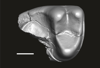
|
M3#1085Trigonid of a right lower molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1085 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2230 View specimen
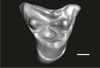
|
M3#1086Right DP4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1086 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2228 View specimen
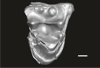
|
M3#1093Right M1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1093 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2229 View specimen
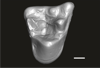
|
M3#1087Right M2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1087 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2236 View specimen
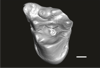
|
M3#1088Left M2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1088 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2231 View specimen
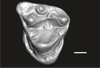
|
M3#1089Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1089 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2232 View specimen
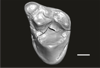
|
M3#1090Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1090 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2234 View specimen
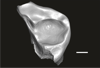
|
M3#1091Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1091 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2233 View specimen
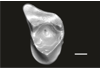
|
M3#1092Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1092 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models of the enamel-dentine junctions of upper third molars and of the bony labyrinths of the extant cercopithecoid specimens analyzed in the following publication: Beaudet, A., Dumoncel, J., Thackeray, J.F., Bruxelles, L., Duployer, B., Tenailleau, C., Bam, L., Hoffman, J., de Beer, F., Braga, J.: Upper third molar internal structural organization and semicircular canal morphology in Plio-Pleistocene South African cercopithecoids. Journal of Human Evolution 95, 104-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2016.04.004
Cercocebus atys 81.007-M-0041 View specimen
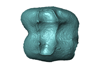
|
M3#4453D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.445 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cercocebus torquatus 73.018-M-0359 View specimen
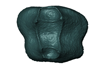
|
M3#4463D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.446 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4963D model of the left bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.496 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mandrillus leucophaeus 73.029-M-0106 View specimen

|
M3#4473D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.447 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4703D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.470 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Lophocebus albigena 73.029-M-0109 View specimen
|
M3#4483D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.448 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4713D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.471 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Piliocolobus foai 91.060-M-0071 View specimen
|
M3#4493D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.449 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4723D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.472 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Colobus guereza 1215 View specimen
|
M3#4503D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.450 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4733D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.473 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Colobus guereza 2800 View specimen
|
M3#4513D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.451 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4743D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.474 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Papio cynocephalus kindae 3503 View specimen
|
M3#4523D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.452 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4753D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.475 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Erythrocebus patas 8452 View specimen

|
M3#4533D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.453 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4763D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.476 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Papio cynocephalus kindae 17979 View specimen
|
M3#4543D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.454 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4773D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.477 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Colobus angolensis 25456 View specimen

|
M3#4553D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.455 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4783D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.478 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Chlorocebus pygerythrus 37477 View specimen
|
M3#4563D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.456 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4813D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.481 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Chlorocebus pygerythrus 37478 View specimen

|
M3#4573D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.457 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4823D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.482 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Lophocebus albigena 37572 View specimen
|
M3#4583D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.458 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4833D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.483 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Lophocebus albigena 37579 View specimen

|
M3#4593D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.459 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Erythrocebus patas OST.2002-26 View specimen

|
M3#4603D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.460 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4843D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.484 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mandrillus sphinx OST.AC.488 View specimen
|
M3#4613D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.461 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4853D model of the left bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.485 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Macaca mulatta OST.AC.492 View specimen

|
M3#4623D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.462 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4863D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.486 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Chlorocebus aethiops OST.AC.523 View specimen

|
M3#4633D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.463 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4913D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.491 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cercopithecus cephus OST.AC.533 View specimen
|
M3#4643D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.464 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4933D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.493 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Chlorocebus aethiops OST.AC.540 View specimen
|
M3#4653D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.465 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4943D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.494 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mandrillus sphinx OST.AC.543 View specimen

|
M3#4663D model of the enamel-dentine junction of the right upper third molar. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.466 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#4953D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.495 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cercocebus torquatus 73.018-M-389 View specimen

|
M3#4683D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.468 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mandrillus leucophaeus 73.029-M-0105 View specimen

|
M3#4693D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.469 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mandrillus leucophaeus 28425 View specimen

|
M3#4793D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.479 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cercocebus atys 28998 View specimen

|
M3#4803D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.480 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Macaca sylvanus OST.AC.493 View specimen

|
M3#4873D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.487 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Chlorocebus aethiops OST.AC.508 View specimen

|
M3#4883D model of the left bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.488 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cercopithecus cephus OST.AC.515 View specimen

|
M3#4893D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.489 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Colobus guereza OST.AC.519 View specimen

|
M3#4903D model of the right bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.490 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Macaca sp. OST.AC.532 View specimen

|
M3#4923D model of the left bony labyrinth. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.492 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
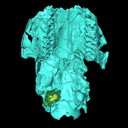
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models of the holotype (NMB Sth. 833) of the new species Micromeryx? eiselei analysed in the article Aiglstorfer, M., Costeur, L., Mennecart, B., Heizmann, E.P.J.. 2017. Micromeryx? eiselei - a new moschid species from Steinheim am Albuch, Germany, and the first comprehensive description of moschid cranial material from the Miocene of Central Europe. PlosOne https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185679
Micromeryx? eiselei NMB Sth. 833 View specimen
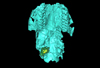
|
M3#284The 3 D surfaces comprises the skull, petrosal, and bony labyrinth of NMB Sth.833, the holotype of Micromeryx? eiselei Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.284 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
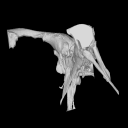
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in: Perrichon et al., 2023. Neuroanatomy and pneumaticity of Voay robustus and its implications for crocodylid phylogeny and palaeoecology.
Crocodylus niloticus MHNL 50001387 View specimen

|
M3#1202Skull, inner ear, pharyngotympanic sinus and neurovascular system Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1202 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Voay robustus MNHN F.1908-5 View specimen
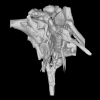
|
M3#1203Skull, inner ear, pharyngotympanic sinus and neurovascular system Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1203 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Voay robustus NHMUK PV R 36684 View specimen

|
M3#1204Skull, inner ear, pharyngotympanic sinus and neurovascular system Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1204 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Voay robustus NHMUK PV R 36685 View specimen

|
M3#1205Skull, inner ear, pharyngotympanic sinus and neurovascular system Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1205 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Osteolaemus tetraspis UCBLZ 2019-1-236 View specimen
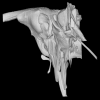
|
M3#1208Skull, inner ear, pharyngotympanic sinus and neurovascular system Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1208 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mecistops sp. UM N89 View specimen

|
M3#1207Skull, inner ear, pharyngotympanic sinus and neurovascular system Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1207 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Voay robustus NHMUK PV R 2204 View specimen

|
M3#1206Skull, inner ear, pharyngotympanic sinus, intertympanic sinus and neurovascular system Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1206 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
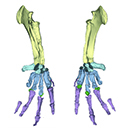
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D model analyzed in Vautrin et al. (2019), Palaeontology, From limb to fin: an Eocene protocetid forelimb from Senegal sheds new light on the early locomotor evolution of early cetaceans.
?Carolinacetus indet. SNTB 2011-01 View specimen
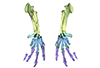
|
M3#3983D model of an articulated forelimb of a Carolinacetus-like protocetid from Senegal Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.398 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models of external and internal aspects of human upper permanent second molars from the Neolithic necropolis analyzed in the following publication: Le Luyer M., Coquerelle M., Rottier S., Bayle P. (2016): Internal tooth structure and burial practices: insights into the Neolithic necropolis of Gurgy (France, 5100-4000 cal. BC). Plos One 11(7): e0159688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159688.
Homo sapiens GLN04-201-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#74Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.74 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-206-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#75Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.75 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-213-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#76Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.76 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-215A-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#77Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.77 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN06-215B-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#78Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.78 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN06-223-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#79Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.79 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-229-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#80Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.80 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-243B-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#81Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) with reconstructed dentine horn tip of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.81 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-248-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#82Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) with reconstructed dentine horn tip of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.82 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-252-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#83Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.83 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-253-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#84Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.84 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-257-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#85Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) with reconstructed dentine horn tip of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.85 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-264-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#86Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.86 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-277-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#87Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.87 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN04-289B-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#88Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.88 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN06-291-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#89Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) with reconstructed dentine horn tip of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.89 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-292-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#90Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.90 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-294-ULM2 View specimen
|
M3#91Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) with reconstructed dentine horn tip of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.91 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-308-URM2 View specimen

|
M3#93Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent right second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.93 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens GLN05-301-ULM2 View specimen

|
M3#92Outer enamel surface (OES) and enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) of Neolithic upper permanent left second molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.92 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

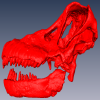
The study of titanosaur paleobiology has been severely hampered by the incomplete nature of their fossil record, particularly the scarcity of well-preserved and relatively complete cranial remains. Even the most complete titanosaur skulls are often fractured, incomplete, or deformed, which has resulted in a limited knowledge of the paleobiology related to cranial anatomy, especially functional morphology. In this context, we present the digital restoration of the skull of the Argentinean titanosaur Sarmientosaurus musacchioi, created using the open-source 3D modeling software Blender. The digitally restored model is freely accessible to other researchers, facilitating broader research and comparative studies.
Sarmientosaurus mussacchioi MDT-PV 02 View specimen

|
M3#1594Cranium and mandible of Sarmientosaurus mussacchioi Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1594 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
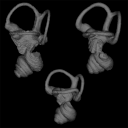
|
M3#1599Original object provided by Gabriel Casal (cranium) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1599 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
This contribution contains the three-dimensional models of the inner ear of the hetaxodontid rodents Amblyrhiza, Clidomys and Elasmodontomys from the West Indies. These specimens were analyzed and discussed in : The inner ear of caviomorph rodents: phylogenetic implications and application to extinct West Indian taxa.
Amblyrhiza inundata 11842 View specimen

|
M3#11543D surface of the left-oriented inner ear of Amblyrhiza. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1154 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Clidomys sp NA View specimen
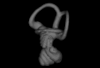
|
M3#11553D surface of the left-oriented inner ear of Clidomys sp. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1155 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Elasmodontomys obliquus 17127 View specimen
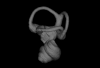
|
M3#11563D surface of the left-oriented inner ear of Elasmodontomys obliquus. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1156 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
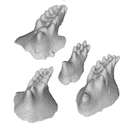
This contribution contains the 3D models of a set of Famennian conodont elements belonging to the species Icriodus alternatus analyzed in the following publication: Girard et al. 2022: Deciphering the morphological variation and its ontogenetic dynamics in the Late Devonian conodont Icriodus alternatus.
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 031 View specimen

|
M3#887conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.887 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 032 View specimen

|
M3#888conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.888 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 033 View specimen

|
M3#889conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.889 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 034 View specimen

|
M3#890conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.890 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 035 View specimen
|
M3#891conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.891 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 036 View specimen

|
M3#892conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.892 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 037 View specimen

|
M3#893conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.893 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 038 View specimen

|
M3#894conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.894 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 039 View specimen

|
M3#895conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.895 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 040 View specimen

|
M3#896conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.896 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 041 View specimen

|
M3#897conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.897 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 042 View specimen

|
M3#898conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.898 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 043 View specimen

|
M3#899conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.899 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 044 View specimen

|
M3#900conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.900 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Icriodus alternatus UM BUS 045 View specimen

|
M3#901conodont element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.901 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

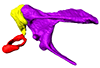
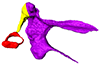
Considerable morphological variations are found in the middle ear among mammals. Here I present a three-dimensional atlas of the middle ear ossicles of eulipotyphlan mammals. This group has radiated into various environments as terrestrial, aquatic, and subterranean habitats independently in multiple lineages. Therefore, eulipotyphlans are an ideal group to explore the form-function relationship of the middle ear ossicles. This comparative atlas of hedgehogs, true shrews, water shrews, mole shrews, true moles, and shrew moles encourages future studies of the middle ear morphology of this diverse group.
Erinaceus europaeus DK2331 View specimen
|
M3#151Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.151 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Anourosorex yamashinai SIK_yamashinai View specimen
|
M3#152Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.152 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Blarina brevicauda M8003 View specimen
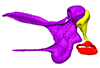
|
M3#153Right middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.153 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Chimarrogale platycephala DK5481 View specimen
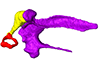
|
M3#162Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.162 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Suncus murinus DK1227 View specimen
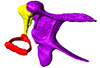
|
M3#155Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.155 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Condylura cristata SIK0050 View specimen
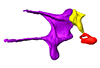
|
M3#156Right middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.156 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Euroscaptor klossi SIK0673 View specimen
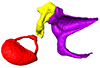
|
M3#163Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.163 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Euroscaptor malayana SIK_malayana View specimen
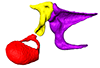
|
M3#164Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.164 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mogera wogura DK2551 View specimen

|
M3#159Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.159 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Talpa altaica SIK_altaica View specimen

|
M3#161Right middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.161 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Urotrichus talpoides DK0887 View specimen

|
M3#165Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.165 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Oreoscaptor mizura DK6545 View specimen
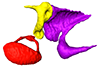
|
M3#166Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.166 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Scalopus aquaticus SIK_aquaticus View specimen
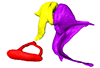
|
M3#167Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.167 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Scapanus orarius SIK_orarius View specimen

|
M3#168Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.168 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Neurotrichus gibbsii SIK_gibbsii View specimen
|
M3#169Left middle ear ossicles Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.169 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
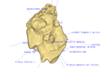
This contribution contains the 3D models described and figured in the following publication: Mourlam, M., Orliac, M. J. (2017), Protocetid (Cetacea, Artiodactyla) bullae and petrosals from the Middle Eocene locality of Kpogamé, Togo: new insights into the early history of cetacean hearing. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology https://doi.org/10.1080/14772019.2017.1328378
?Carolinacetus indet. UM KPG-M 164 View specimen
|
M3#132left petrosal of ?Carolinacetus sp. from the locality of Kpogamé, Togo Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.132 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
indet. indet. UM KPG-M 73 View specimen
|
M3#133labelled surface of the left petrosal Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.133 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#134left bullaof Protocetidae indeterminate from Kpogamé, Togo Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.134 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
|
M3#135petrotympanic complex of Protocetidae indeterminate from Kpogamé, Togo Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.135 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
?Carolinacetus indet. UM KPG-M 33 View specimen

|
M3#136left auditory bulla of a juvenile specimen of ?Carolinacetus sp. from Kpogamé, Togo Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.136 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Togocetus traversei UM KPG-M 80 View specimen

|
M3#137fragmentary right auditory bulla of Togocetus traversei from Kpogamé, Togo Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.137 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
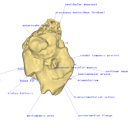
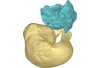
This project presents the 3D models of two isolated petrosals from the Oligocene locality of Pech de Fraysse (Quercy, France) here attributed to the genus Prodremotherium Filhol, 1877. Our aim is to describe the petrosal morphology of this Oligocene “early ruminant” as only few data are available in the literature for Oligocene taxa.
Prodremotherium sp. UM PFY 4053 View specimen
|
M3#7Labelled 3D model of right isolated petrosal of Prodremotherium sp. from Pech de Fraysse (Quercy, MP 28) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf7 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Prodremotherium sp. UM PFY 4054 View specimen

|
M3#8Labelled 3D model of right isolated petrosal of Prodremotherium sp. from Pech de Fraysse (Quercy, MP 28) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf8 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
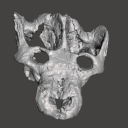
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models of a skull and lower jaw of the holotype of Santagnathus mariensis, described in “Old fossil findings in the Upper Triassic rocks of southern Brazil improve diversity of traversodontid cynodonts (Therapsida, Cynodontia)”
Santagnathus mariensis UFRGS-PV-1419-T View specimen
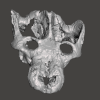
|
M3#1157Skull Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1157 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#1158Lower jaw Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1158 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
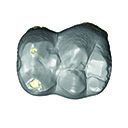
This contribution contains the 3D models described and figured in the following publication: Hautier L, Tabuce R, Kassegne KE, Amoudji YZ, Mourlam M, Orliac M, Quillévéré F, Charruault A-L, Johnson AKC, Guinot G. 2021. New middle Eocene proboscidean from Togo illuminates the early evolution of the elephantiform-like dental pattern.
Dagbatitherium tassyi ULDG-DAG1 View specimen
|
M3#7693D model of a molar of Dagbatitherium tassyi. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.769 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
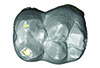
|
M3#771µCT scan of a molar of Dagbatitherium tassyi. Type: "3D_CT"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.771 state:published |
Download CT data |
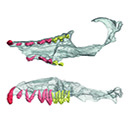
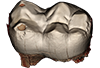
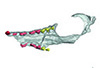
This contribution contains the 3D models described and figured in the following publication: Kassegne K. E., Mourlam M. J., Guinot G., Amoudji Y. Z., Martin J. E., Togbe K. A., Johnson A. K., Hautier L. 2021. First partial cranium of Togocetus from Kpogamé (Togo) and the protocetid diversity in the Togolese phosphate basin. Annales de Paléontologie, Issue 2, April–June 2021, 102488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annpal.2021.102488
Togocetus cf. traversei ULDG-KPO1 View specimen
|
M3#768The specimen consists of a partial cranium prepared out of a calcareous phosphate matrix. The partial cranium lacks the anterior part of the rostrum, the cranial roof, and most of the basicranium apart from the left zygomatic process of the squamosal. The maxilla, nasal, palatine, pterygoid, alisphenoid, and squamosal bones are preserved, as well as two incomplete dental rows described hereafter. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.768 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#770µCT . Resolution: 0.3156mm. This scan can easily be opened with Fiji, MorphoDig, 3DSlicer, or any software that reads .MHD file format. Also, the .RAW file can be opened easily with other software such as Avizo/Amira when providing the correct dimensions (which are enclosed within the file name) Type: "3D_CT"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.770 state:published |
Download CT data |
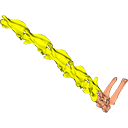
This contribution contains the 3D models analyzed in Müller et al. (2021) “Pushing the boundary? Testing the ‘functional elongation hypothesis’ of the giraffe’s neck”.
Aepyceros melampus ZFMK 2001.278 View specimen
|
M3#643Vertebrae C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.643 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis ZMB 66393 View specimen
|
M3#644Vertebrae Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.644 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis ZSM 1967/17 View specimen
|
M3#645Vertebrae Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.645 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis ZSM 1981/19 View specimen
|
M3#646C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.646 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis KMDA M-10861 View specimen
|
M3#647C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2. Acquired via laser scanner. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.647 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis SMF 84214 View specimen
|
M3#648C7, T1. Warning : photogrammetric models (unit scale is CM, not MM). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.648 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis SMF 78299 View specimen
|
M3#649C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.649 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis SMF o. N View specimen
|
M3#650C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.650 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Giraffa camelopardalis SMNS 19138 View specimen
|
M3#671C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.671 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Okapia johnstoni ZMB 62086 View specimen
|
M3#651C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.651 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Okapia johnstoni ZMB 70325 View specimen
|
M3#652C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.652 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Sivatherium giganteum NHMUK 15707 View specimen
|
M3#653C7. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D model (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.653 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Sivatherium giganteum NHMUK 15297 View specimen
|
M3#654T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D model (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.654 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cervus elaphus ZMB 47502 View specimen
|
M3#655C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.655 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Axis axis SMF 1450 View specimen
|
M3#656C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.656 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cervus nippon SMF 4368 View specimen
|
M3#657C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.657 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Capreolus capreolus SMF 79852 View specimen

|
M3#658C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.658 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Capreolus capreolus ZFMK 67.237 View specimen

|
M3#659C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.659 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Muntiacus reevesi SMF 92954 View specimen
|
M3#660C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.660 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Muntiacus reevesi SMF 92332 View specimen
|
M3#661C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.661 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Alces alces SMF 35549 View specimen
|
M3#662C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.662 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Dama dama ZFMK 86.125 View specimen

|
M3#663C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.663 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Antilope cervicapra ZMB 78829 View specimen

|
M3#664C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.664 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Bison bonasus SMNS 2998 View specimen
|
M3#665C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.665 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Nanger dama SMF 74435 View specimen
|
M3#666C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.666 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Litocranius walleri SMF 23747 View specimen

|
M3#667C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.667 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Litocranius walleri SMF 23749 View specimen

|
M3#669C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.669 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Tragelaphus eurycerus SMF 95875 View specimen
|
M3#670C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.670 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Bos javanicus SMF 64934 View specimen
|
M3#672C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.672 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Ovis aries ZFMK 1982.338 View specimen
|
M3#673C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.673 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Rupicapra rupicapra ZFMK 72.367 View specimen
|
M3#674C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.674 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Kobus ellipsiprymnus SMNS 4443 View specimen
|
M3#675C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.675 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Sylvicapra grimmia SMNS 15292 View specimen
|
M3#676C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.676 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Syncerus caffer SMNS 7347 View specimen
|
M3#677C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.677 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Procapra gutturosa SMNS 5796 View specimen
|
M3#678C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.678 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Damaliscus pygargus SMNS 21617 View specimen
|
M3#679C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.679 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Madoqua kirkii SMNS 4432 View specimen
|
M3#680C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.680 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Bubalus mindorensis SMNS 2054 View specimen
|
M3#681C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.681 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Capra hircus SMNS 51328 View specimen
|
M3#682C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.682 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Connochaetes taurinus SMNS 4442 View specimen
|
M3#683C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.683 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Antilocapra americana ZSM 1964/218 View specimen
|
M3#684C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.684 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Antilocapra americana ZMB 77281 View specimen
|
M3#685C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.685 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Moschus moschiferus ZMB 62080 View specimen
|
M3#686C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, T1, T2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.686 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Moschus moschiferus ZMB 60367 View specimen
|
M3#687C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.687 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Moschus moschiferus ZMB 51830 View specimen
|
M3#688C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.688 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Tragulus javanicus SMF 82179 View specimen
|
M3#689C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.689 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Tragulus javanicus ZMB 86222 View specimen
|
M3#690C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.690 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Tragulus sp. ZMB o. N. View specimen
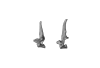
|
M3#691C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.691 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Hyemoschus aquaticus ZMB 71071 View specimen
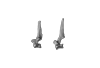
|
M3#692C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.692 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Hyemoschus aquaticus ZMB 103235 View specimen
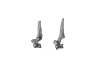
|
M3#693C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.693 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Vicugna vicugna SMF 94752 View specimen
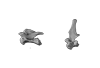
|
M3#694C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.694 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Camelus dromedarius SMF 70473 View specimen
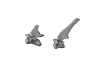
|
M3#695C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.695 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Camelus bactrianus SMF 25542 View specimen

|
M3#696C7, T1. Warning : unscaled photogrammetric 3D models (unknown size). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.696 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Lama glama SMNS 31175 View specimen
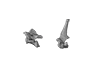
|
M3#697C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.697 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Vicugna pacos SMNS 46255 View specimen

|
M3#698C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.698 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Vicugna pacos SMNS 7349 View specimen

|
M3#699C7, T1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.699 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |